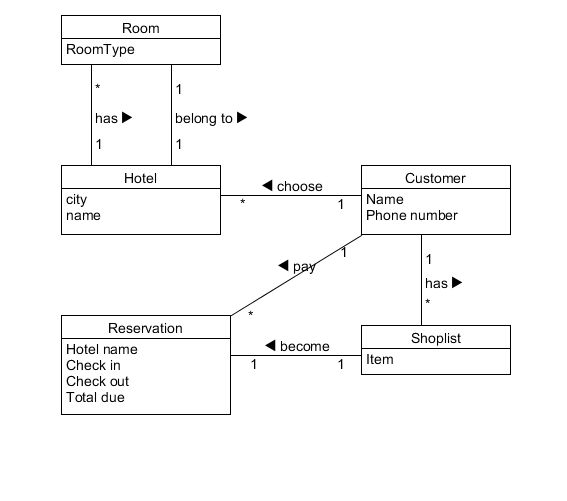
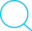
一、领域建模
a. 阅读 Asg_RH 文档,按用例构建领域模型。
按 Task2 要求,请使用工具 UMLet,截图格式务必是 png 并控制尺寸
说明:请不要受 PCMEF 层次结构影响。你需要识别实体(E)和 中介实体(M,也称状态实体)
在单页面应用(如 vue)中,E 一般与数据库构建有关, M 一般与 store 模式 有关
在 java web 应用中,E 一般与数据库构建有关, M 一般与 session 有关
b. 数据库建模(E-R 模型)
- 按 Task 3 要求,给出系统的 E-R 模型(数据逻辑模型)
- 建模工具 PowerDesigner(简称PD) 或开源工具 OpenSystemArchitect
- 不负责的链接 http://www.cnblogs.com/mcgrady/archive/2013/05/25/3098588.html
- 导出 Mysql 物理数据库的脚本
drop table if exists Bill;
drop table if exists Credit_Card;
drop table if exists Hotel;
drop table if exists Reservation;
drop table if exists Room;
drop table if exists Traveler;
create table Bill
(
Price double,
Email text,
Card_Number text,
Bill_Number text not null,
Reservation_Number text not null,
primary key (Bill_Number)
);
create table Credit_Card
(
Card_Number text not null,
Owner text,
Saving double,
Security_Code text,
primary key (Card_Number)
);
create table Hotel
(
Hotel_Name text not null,
City text,
Address text not null,
primary key (Hotel_Name, Address)
);
create table Reservation
(
Room_Number text not null,
Check_In date not null,
Check_Out date not null,
Hotel_Name text not null,
Address text not null,
Adult_Count int,
Child_Count int,
Child_Age int,
Price double,
Traveler_Name text,
Reservation_Number text not null,
Bill_Number text not null,
primary key (Reservation_Number)
);
create table Room
(
Room_Number text not null,
Hotel_Name text,
Address text,
Availability bool,
primary key (Room_Number)
);
create table Traveler
(
Name text,
Email text not null,
Smoking bool,
primary key (Email)
);
alter table Bill add constraint FK_Reference_3 foreign key (Email)
references Traveler (Email) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Bill add constraint FK_Reference_4 foreign key (Card_Number)
references Credit_Card (Card_Number) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Bill add constraint FK_Reference_6 foreign key (Reservation_Number)
references Reservation (Reservation_Number) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Reservation add constraint FK_Reference_1 foreign key (Room_Number)
references Room (Room_Number) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Reservation add constraint FK_Reference_5 foreign key (Hotel_Name, Address)
references Hotel (Hotel_Name, Address) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Reservation add constraint FK_Reference_6 foreign key (Bill_Number)
references Bill (Bill_Number) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Room add constraint FK_Reference_2 foreign key (Hotel_Name, Address)
references Hotel (Hotel_Name, Address) on delete restrict on update restrict;
- 简单叙说 数据库逻辑模型 与 领域模型 的异同
领域模型(概念模型)就是在了解了用户的需求,用户的业务领域工作情况以后,经过分析和总结,提炼出来的用以描述用户业务需求的一些概念的东西。(此时可以不包含属性,只有实体集,联系集的分析结构)
逻辑模型:是将概念模型转化为具体的数据模型的过程,即按照概念结构设计阶段建立的基本E-R图,按选定的管理系统软件支持的数据模型(层次、网状、关系、面向对象),转换成相应的逻辑模型。这种转换要符合关系数据模型的原则。目前最流行就是关系模型(也就是对应的关系数据库)。
概念模型是最终用户对数据存储的看法,反映了最终用户综合性的信息需求,它以数据类的方式描述企业级的数据需求,数据类代表了在业务环境中自然聚集成的几个主要类别数据。概念模型的内容包括重要的实体及实体之间的关系。在概念数据模型中不包括实体的属性 ,也不用定义实体的主键。这是概念数据模型和逻辑数据模型的主要区别。
逻辑模型反映的是系统分析设计人员对数据存储的观点,是对概念数据模型进一步的分解和细化。逻辑模型是根据业务规则确定的,关于业务对象、业务对象的数据项及业务对象之间关系的基本蓝图。逻辑数据模型的内容包括所有的实体和关系,确定每个实体的属性,定义每个实体的主键,指定实体的外键,需要进行范式化处理。逻辑数据模型的目标是尽可能详细的描述数据,但并不考虑数据在物理上如何来实现。